How can one plant compound, cannabidiol (CBD), help with so many different aspects of our well-being—from mood and sleep to pain and inflammation? The answer lies not in the plant itself, but within our own bodies. The answer is the Endocannabinoid System.
Discovered in the 1990s, the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is now considered one of the most important physiological systems in the human body. Think of it as your body’s master regulator, constantly working to maintain balance. This article will explain what the ECS is, its components, and the sophisticated way CBD interacts with it to support your health.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The primary job of the ECS is to maintain homeostasis—the maintenance of a stable internal environment despite fluctuations in the outside world. It helps regulate a vast range of our body’s processes, including:
- Mood and stress response
- Sleep cycles
- Appetite and metabolism
- Pain perception and inflammation
- Memory and learning
- Immune function
When an outside force, like an injury or stress, throws your body out of balance, the ECS steps in to help it return to its ideal state.
The Three Core Components of the ECS
The ECS is a complex network, but it can be broken down into three simple parts:
1. Cannabinoid Receptors (The “Docking Stations”)
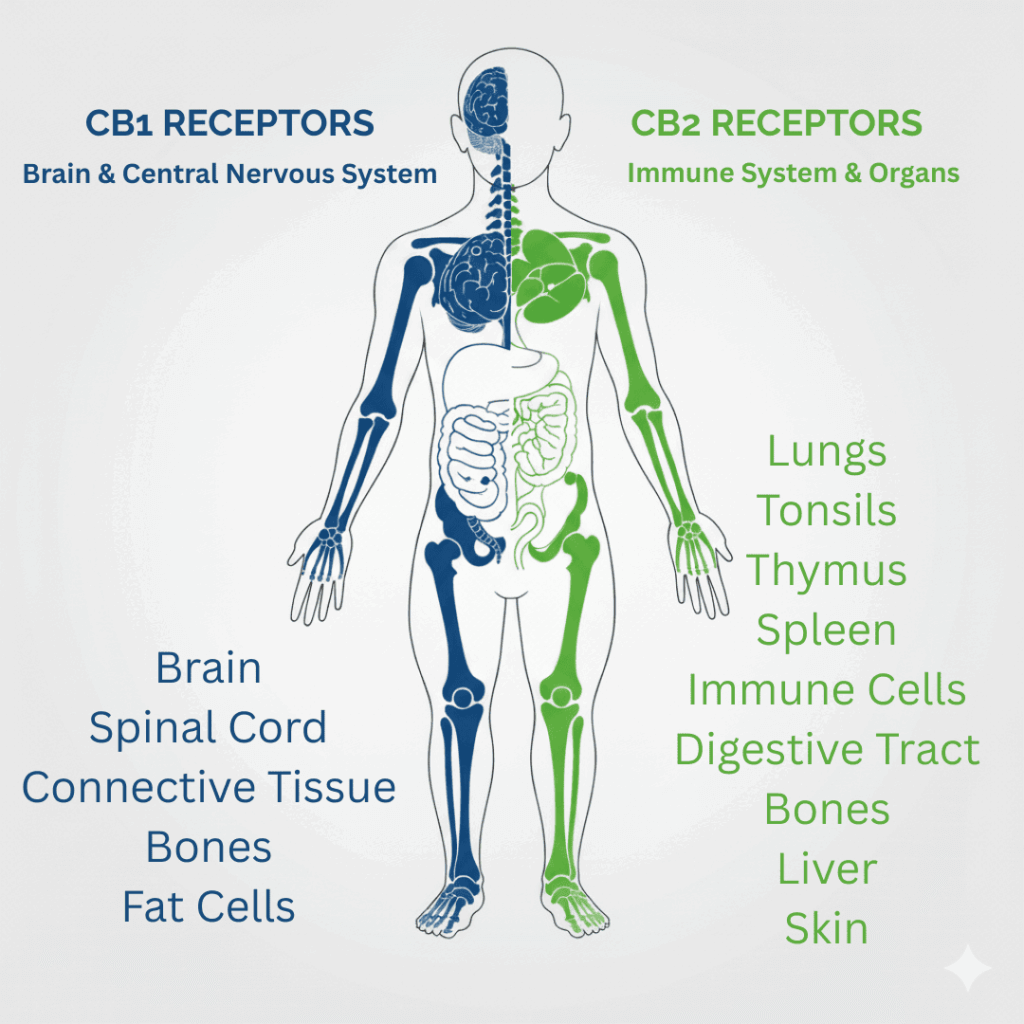
These are receptors found on the surface of cells throughout your body. They act like locks, waiting for the right key to activate them. The two main receptors are:
- CB1 Receptors: Found mostly in the brain and central nervous system. They are involved in mood, memory, and pain perception. THC binds directly to these receptors, which is what produces a psychoactive “high.”
- CB2 Receptors: Found mainly in the immune system and peripheral tissues. They are key players in managing inflammation and immune response.
A powerful example of CB1 receptors in action is their role in extinguishing traumatic or fearful memories. Foundational research from 2012 first explored how cannabinoids could help with this process, and these findings have been strengthened by more recent studies, like this comprehensive 2025 meta-analysis, which confirmed CBD’s effectiveness anxiety and stress-related disorders.
2. Endocannabinoids (The Body’s “Messengers”)
These are the keys to the locks. “Endo” means “within,” as these are cannabinoids produced by your own body. The two most well-known are:
- Anandamide: Often called the “bliss molecule” for its role in mood and well-being.
- 2-AG: The most abundant endocannabinoid, involved in everything from appetite to pain sensation.
Your body creates these on-demand to bind with CB1 or CB2 receptors and signal that an action is needed (e.g., “calm down this inflammatory response”).
3. Metabolic Enzymes (The “Cleanup Crew”)
These enzymes are responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids after they’ve been used. The most important one to know is FAAH, which specifically breaks down Anandamide.
How CBD Interacts with the ECS
This is where the science gets truly fascinating. Unlike THC, which directly binds to the CB1 receptor, CBD’s role is much more sophisticated and indirect.
CBD has a low affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead of binding to them directly, one of its main actions is to inhibit the FAAH enzyme—the “cleanup crew” for your bliss molecule, Anandamide.
By inhibiting FAAH, CBD allows your own natural endocannabinoids to stay in your system for longer, strengthening their calming and balancing effects. Think of it less like a sledgehammer and more like a skilled conductor, helping your body’s own orchestra play in perfect harmony.
Furthermore, modern research shows CBD also influences other important non-cannabinoid receptors, including serotonin receptors (linked to mood) and TRPV1 vanilloid receptors (linked to pain signaling), which helps explain its wide range of benefits.
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in Your Health
The primary goal of the endocannabinoid system is a single, crucial task: to maintain homeostasis, or balance, across all of your body’s complex functions. Think of it as a highly intelligent internal regulator, constantly making adjustments to keep you in your optimal zone. It achieves this using the messengers it creates itself.
As we covered, your body’s two main endocannabinoids are Anandamide and 2-AG. To be more specific, these are endogenous arachidonate-based lipids: anandamide (N-arachidonoylethanolamide, AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). Unlike traditional neurotransmitters, they are created “on-demand” exactly where needed, traveling backward across synapses to deliver instructions like “calm down,” “reduce inflammation,” or “stop sending pain signals.”
But what happens when the body doesn’t produce enough of these essential compounds or has an imbalance in its ECS tone? This leads to a prominent theory known as Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency (CECD). Researchers have proposed that a deficient ECS may be the underlying cause of a number of treatment-resistant conditions, including fibromyalgia, migraines, and IBS. In these cases, supplementing with plant-based cannabinoids like CBD may help support a deficient ECS and guide the body back toward homeostasis.
Conclusion: Supporting Your Body’s Balance
The Endocannabinoid System is the bridge between the body and the benefits of CBD. CBD works not by forcing an action, but by intelligently supporting your body’s innate ability to find balance. This is why a high-quality, whole-flower product is so effective—it provides the ECS with a full spectrum of compounds to work with, promoting overall health and well-being as nature intended.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Please consult with your healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen.
Get Science-Backed Wellness Insights
Sign up for our newsletter to receive the latest research, wellness tips, and product updates delivered directly to your inbox.